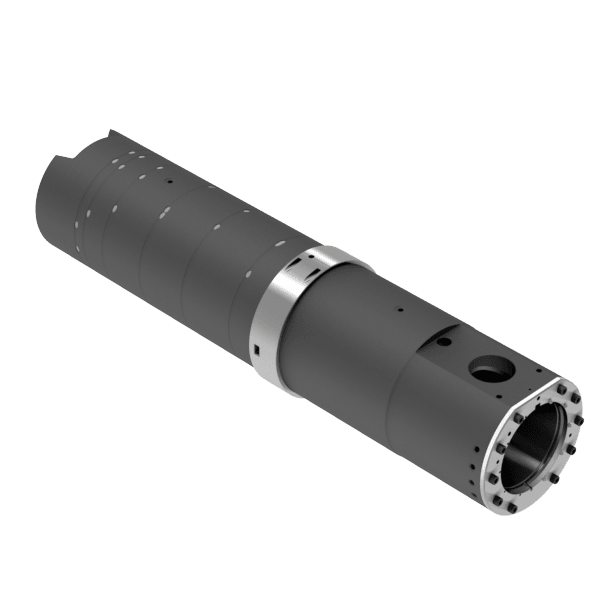
The shot sleeve is a critical element of the aluminum die cast process. To maximize productivity and longevity, the plunger must move smoothly and steadily through a perfectly round, straight shot sleeve.
This does not always happen however, because when heated, metal expands. If partially filled with hot molten alloy, the shot sleeve will become distorted. Our experts at Castool use simulation tools to mimic the process of casting and make sure the distortion of the sleeve is within the limits on each new design.
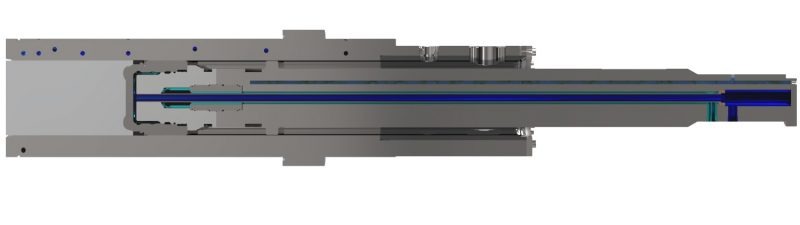

Typically, a shot sleeve may become 100-150° C (200-300° F) hotter at the bottom under the pour hole, than at the top in front of the hole. If the temperature of the sleeve is much higher at the bottom than at the top, unequal expansion will cause it to become oval instead of round. This will also cause the sleeve to become slightly bowed rather than straight. This results in allowing some of the alloy to enter part of the gap between the plunger and the sleeve, affecting the seal between the plunger and shot sleeve, and leading to premature wear and inconsistent shot velocity.
The temperature of a sleeve surface directly under the pour hole can reach as high as 680° C during pouring for structural alloys, for example Silafont. At such a high temperature the integrity of nitride and steel is destroyed. Castool collaborates with a steel manufacturer to create Tuff Temper (TT), which is modified premium W.Nr. 1.2367 steel. The Tuff Temper steel has higher Molybdenum content. The high Molybdenum content increases the corrosion resistance and soldering resistance. The tempering resistance of TT is 45° C higher than W.Nr. 1.2344(H-13). The Tuff Temper sleeve insert reduces the total crack length by 50% than W. Nr. 1.2344(H-13). The TT permits higher temperature nitride treatment and more thermally stable nitride.
The shot sleeve design should incorporate a wall thickness 1/3 of the bore, and the pour spout of no more than 2/3 of the bore.
H-13 (1.2344), Tuff-Temper, Con-Duct Heat Treated, Nitrided and 3P Coated
NEW SHOT SLEEVE INSERT
- Castool offers replaceable inserts for shot sleeves when erosion is the main cause of wear
- Castool has added a post-nitriding process we call 3P, which has extended the insert life
- With advanced manufacturing techniques, there are no fit problems as in the past.
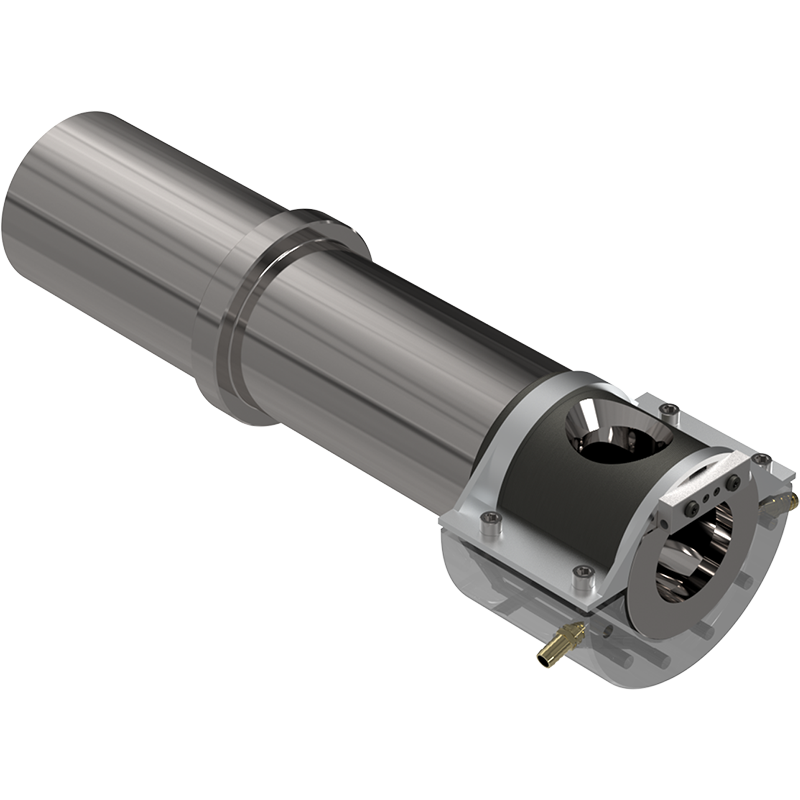

Medium diameter shot sleeves may require thermal control depending on the application, and when necessary can often use an external cooling saddle. The pour end of the shot sleeve where the temperature is highest, is obviously where cooling is most necessary. Accordingly, the pour-end cooling saddle effectively and economically puts shot sleeve cooling where it is needed most, directly below the pour spout.
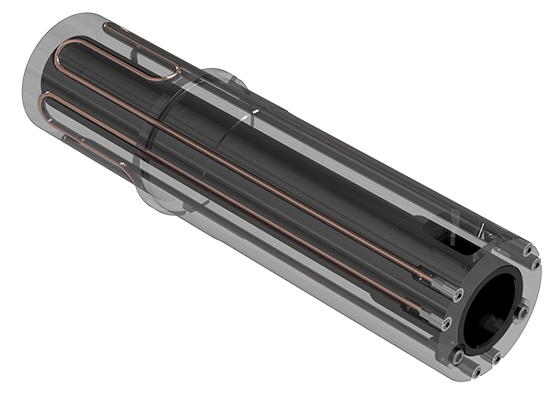
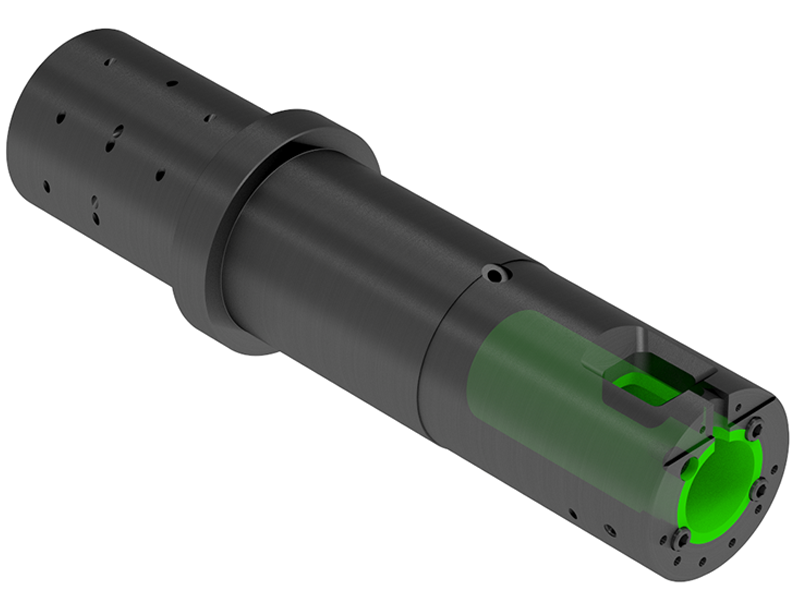
A safe alternative to gun-drilling is using partial or complete M-Loop.
Copper tubes are embedded in the outside diameter of the shot sleeve.
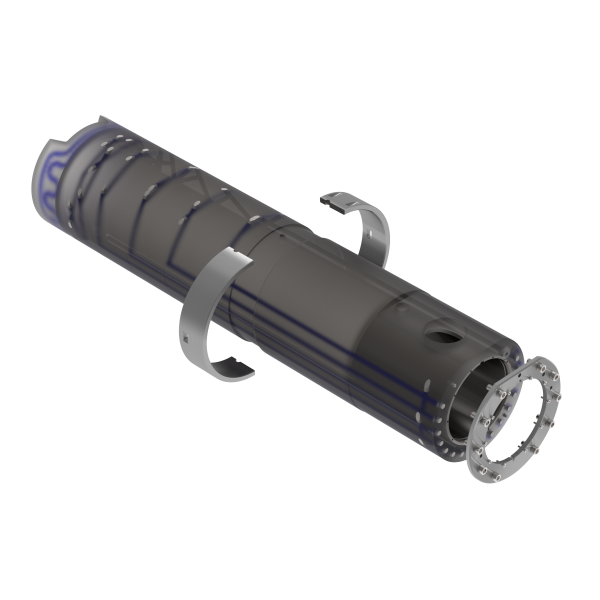

For larger shot sleeves, to avoid too much variation in thermal expansion, a series of gun-drilled holes are located along the length of the shot sleeve under the pour spout, and connected to similar holes around the die end of the shot sleeve.
In most cases where vacuum is being used, it is necessary to use a thermally controlled shot sleeve.
A thermal control unit can be used to manage the temperature and flow of a medium, usually oil, to improve control of the shot sleeve temperature and dimensions during production
Purpose
- Stabilize temperatures to maintain a round and straight shot sleeve, so that the plunger tip can seal on to the shot sleeve wall, extending tooling life
- Allow plunger to move through the shot sleeve smoothly and consistently, reducing scrap
- Provide a long life, minimizing unscheduled downtime
Function
- The function of the shot sleeve is to contain the molten aluminum being pushed into the mold by the plunger tip.
- Reduces scrap and unscheduled downtime.
- Aids consistent shot velocity.
- Extends life of shot sleeve.
- Extends life of plunger tip.
- Cooling can be automatically controlled.



